- the frequency of the wave (in )
- is the angular frequency of the wave (in )
- is the period of the wave (in )
- is the wave speed of the wave (in )
- is the wavelength of the wave (in )
- is the wavenumber (in )
Energy Transport
- ( is the wave intensity, the power transported per unit area perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation)
- (i.e. the intensity is proportional to the square of the amplitude)
Waveform
Sine wave
-
A sine wave (or sinusoidal wave or sinusoid) (symbol: ∿) is any function of the form
- A sine wave is a periodic function with period , amplitude , and phase shift .
- is the equation of a traveling wave (to the right. if it is to the left, the minus sign is replaced by a plus sign)
- is the position of the wave we are considering
- is the distance the wave has traveled from the origin at time
-
A harmonic is a sine wave whose frequency is an integer multiple of the fundamental frequency of a periodic wave.
-
The phasor of a sinusoid is a complex number (also denoted as )
Transverse and longitudinal waves
Transverse wave
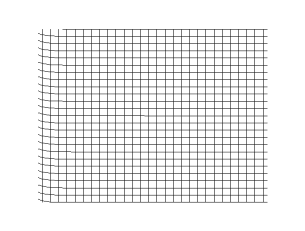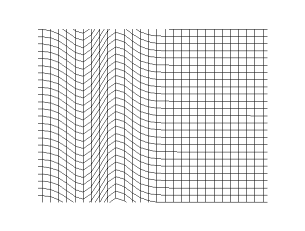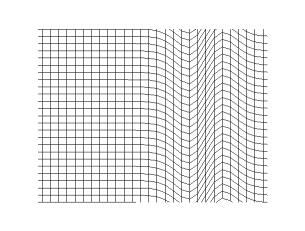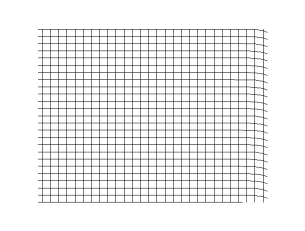
- is the wave speed of a transverse wave traveling along a stretched string of tension (in ) and linear mass density (in )
Longitudinal wave
Standing and traveling waves
Standing wave
- is the frequency of the th harmonic
- is the harmonic number
- is the length of the string
- is the wavelength of the th harmonic
Traveling wave
- (right-moving)
- (left-moving)
Oscillations
-
The natural frequency of an oscillating system is the frequency at which the system oscillates when it is set in motion and left undisturbed.
-
When the natural frequency and the driving frequency are the same or very close, the system exhibits resonance, which results in large amplitude oscillations. (which also depends on the damping)
- At resonance, relatively small forces are required to obtain and maintain large amplitude oscillations.
-
In the presence of a sinusoidal external force, a system may exhibit resonance.
-
Resonance occurs when an external force is exerted at the natural frequency of an oscillating system.
draft
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-j8PzkZ70Lg
-
-
- is representing exponential growth/decay rate
- (exponential growth)
- (exponential decay)
- (constant amplitude)
- is representing exponential growth/decay rate
-
- is representing oscillation (angular frequency)
- is the damping ratio
- (underdamped)
- (critically damped)
- (overdamped)
- (undamped)
Mechanical waves
Sound
- Sound is a longitudinal wave.
- speed of sound
- (e.g. in air at 20\,^\circ\mathrm{C} is , in water is )
- (sound intensity) (in ), where is the sound power (in ) and is the area through which the sound power flows (in )
- (Sound intensity level) (in dB), where is the reference intensity.
- (Sound power level) (in dB), where is the sound power and .
